Evaluate how a rise in foreign direct investment might affect Singapore’s economic performance.
In 2018, Singapore received S$1,737 billion in inward foreign direct investment (FDI), while its outward FDI amounted to S$858 billion. It attracted the highest level of FDI among Southeast Asian countries.
Source: Department of Statistics, Singapore
b. Evaluate how a rise in foreign direct investment might affect Singapore’s economic performance. [15]
Introduction
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to long-term investments by foreign firms or individuals in a country’s businesses, typically in the form of capital investments, acquisitions, or joint ventures. FDI plays a crucial role in enhancing a country’s economic performance by stimulating economic growth, reducing unemployment, influencing inflationary pressures, and affecting the current account balance. As Singapore attracted the highest level of FDI in Southeast Asia in 2018, with inward FDI amounting to S$1.737 trillion, it is important to assess both the positive and potential negative effects of such investments on the country’s economy.
Impact of FDI on Economic Growth
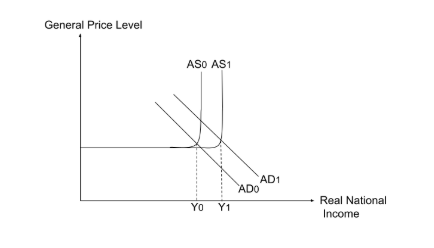
An increase in FDI contributes to both actual and potential economic growth by boosting aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS).
Since FDI falls under the investment (I) component of AD, an increase in FDI leads to a rightward shift in the AD curve, increasing real national income (NY) and stimulating higher economic growth.
Foreign investments often lead to higher capital expenditure on factories, machinery, and technology, which enhances productive capacity and results in a rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve.
If the economy is operating near full employment, the increase in potential output leads to long-term economic growth, allowing Singapore to expand its production frontier.
Therefore, FDI contributes to both short-term expansion through AD growth and long-term economic progress through capital formation and productivity improvements.
Impact of FDI on Unemployment
An increase in FDI has mixed effects on employment, depending on the industries in which investments occur.
1. Reduction in Cyclical Unemployment
Higher FDI leads to increased aggregate demand and economic growth, prompting firms to expand output and hire more workers.
As employment rises, cyclical unemployment declines, benefiting the overall labour market.
2. Risk of Structural Unemployment
FDI often flows into high-value, high-tech, and capital-intensive industries, increasing demand for workers with specialised skills.
However, this may lead to job displacement in traditional industries, as workers in outdated sectors may lack the skills to transition into new industries.
For example, the entry of Grab and Uber into Singapore’s ride-hailing industry created jobs in technology and software development but displaced workers in the traditional taxi sector.
While FDI can reduce unemployment in growing industries, it may also exacerbate structural unemployment, requiring government intervention through retraining programs.
Impact of FDI on Inflation
The impact of FDI on inflation depends on the economy’s capacity to absorb higher aggregate demand.
In the short run, higher FDI leads to increased investment spending, shifting AD to the right. If the economy is already operating near full employment, this could lead to demand-pull inflation, raising the general price level (GPL).
In the long run, however, FDI contributes to capital stock accumulation and technological advancements, shifting LRAS to the right. This expansion in productive capacity helps mitigate inflationary pressures by increasing output efficiency.
Thus, while FDI may initially contribute to inflation, its long-term impact can be deflationary as supply-side improvements take effect.
Impact of FDI on the Current Account Balance
FDI can also have both positive and negative effects on Singapore’s current account, which records trade and income flows between Singapore and the rest of the world.
Short-term effects: FDI inflows initially increase capital inflows, which can improve the overall balance of payments.
Long-term effects: As foreign investors start making profits, they may repatriate earnings to their home countries, leading to increased income outflows from the current account.
Thus, while FDI boosts investment-led economic growth, it can also worsen the current account balance over time if a significant portion of profits is repatriated rather than reinvested locally.
Conclusion
FDI plays a vital role in enhancing Singapore’s economic growth, reducing unemployment, and improving technological advancements, making it a key driver of economic progress. However, it also presents challenges such as structural unemployment, short-term inflationary pressures, and potential current account outflows. While the positive impacts of FDI generally outweigh the negatives, the government must implement policies to mitigate negative effects, such as reskilling displaced workers and ensuring reinvestment of profits within the economy. Overall, FDI remains a crucial pillar of Singapore’s economic success, contributing to both short-term prosperity and long-term competitiveness.
🏁 JC2 Last Lap — Finish Strong, Score Higher
Found this model essay helpful? Now imagine writing like this — consistently and under exam pressure.
At Economics at Tuitiongenius (ETG) — Singapore’s most trusted economics tuition centre — we go beyond showing students the “what”. We teach them the how: how to structure, evaluate, and score at the highest level. With guidance from Mr Eugene Toh, one of the most experienced economics tutors in Singapore, you’ll walk into the A Levels with clarity and control.
🚀 Introducing the JC2 Last Lap Programme
Designed specifically for students sitting the A Levels in a few months, this is your complete H2 economics tuition solution — built for impact.
🎯 What You’ll Get:
✅ 61 JC2 Video Lessons – Full Micro & Macro coverage, accessible anytime
✅ Weekly Live Classes – Choose Zoom or onsite at 4 locations islandwide
✅ 11 Crashcourses Included – Cover essays, CSQs, content gaps and exam strategies
✅ Printed Materials Delivered – Textbooks, summaries, diagrams, evaluation guides
✅ 1-on-1 Consults with Mr Toh – Get your specific questions answered fast
✅ Weekly Homework + Feedback – So every effort leads to measurable improvement
💬 “I scored an E for MYEs… and an A for the A Levels — because of ETG.”
– Wing Ter Tan, Class of 2023
💡 Ideal for:
JC2 students who need structured revision to avoid last-minute panic
Students aiming to break into the A range from a B/C
Those looking for JC economics tuition that includes feedback, flexibility, and proven strategy
If you’re searching for economics tuition Singapore that delivers consistent results — this is your final lap advantage.
🔗 Register now at tuitiongenius.com/lastlap
📲 Or WhatsApp us at 8168 3986 — and we’ll help you take the next step
Your A Level turnaround starts now — let’s cross the finish line together.