Explain the circular flow of income and how an increase in productivity will affect its components.
Productivity forms the foundation for improving a country’s standard of living, as it drives income generation, job creation, and overall economic growth.
a. Explain the circular flow of income and how an increase in productivity will affect its components. [10]
Introduction
Productivity plays a crucial role in driving economic growth and improving the standard of living in a country. Higher productivity enables firms to produce more output with the same or fewer resources, reducing costs and increasing overall efficiency. This, in turn, has significant implications for the circular flow of income, which illustrates how income moves between households, firms, financial institutions, the government, and the foreign sector. An increase in productivity can influence key components of the circular flow by affecting export revenue, investment expenditure, and import expenditure. By reducing production costs, higher productivity enhances the price competitiveness of exports, potentially increasing export revenue. It also boosts business profitability, leading to greater investment expenditure, which serves as an injection into the economy. At the same time, increased productivity can contribute to higher employment and household incomes, which may lead to an increase in import expenditure, causing a leakage from the circular flow. Understanding these effects provides insights into how productivity growth shapes overall economic activity and national income.
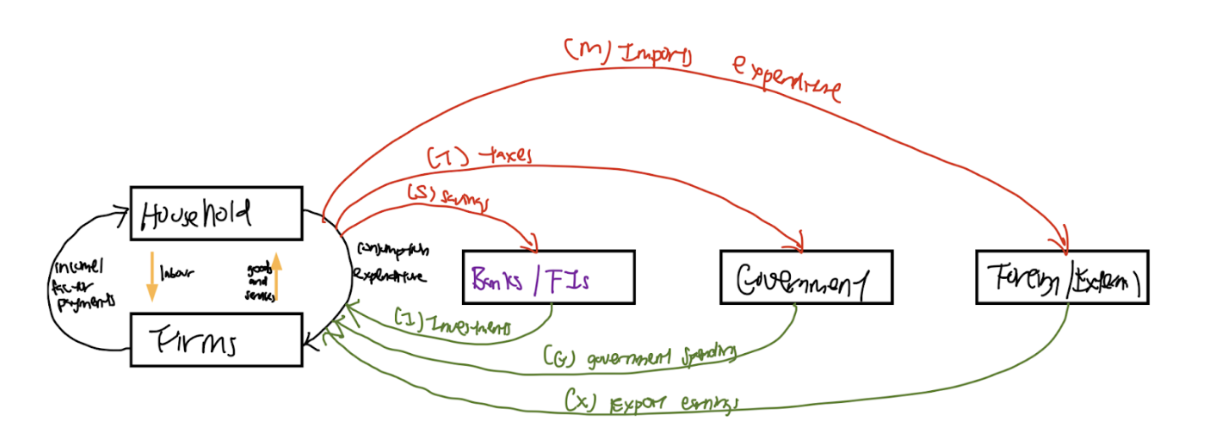
Explain the circular flow of income
The circular flow of income is a fundamental economic model that illustrates the interactions between different economic agents within an economy. It helps explain how income circulates between households, firms, financial institutions, the government, and the foreign sector.
The circular flow consists of two main types of flows: Injections, which introduce income into the economy, and Withdrawals (Leakages), which remove income from the economy.
Injections into the circular flow of income include:
Investment (I): Spending by firms on capital goods such as machinery and infrastructure to enhance production.
Government Expenditure (G): Spending by the government on goods and services, including public infrastructure, healthcare, and education.
Export Earnings (X): Revenue earned from selling domestically produced goods and services to foreign markets.
Withdrawals (Leakages) from the circular flow of income include:
Savings (S): Income that households and firms do not spend on consumption but instead deposit into financial institutions.
Taxes (T): Payments made by households and firms to the government, reducing disposable income and corporate profits.
Import Expenditure (M): Spending on foreign goods and services, which removes money from the domestic economy.
Explain how the circular flow of income works
The circular flow begins with households providing labour to firms. Firms use this labour to produce goods and services, which are then sold to households. In return, firms pay households wages, salaries, and other forms of income, which households then use to purchase goods and services, thereby sustaining economic activity.
Financial institutions play a crucial role in the circular flow by acting as intermediaries between households and firms. Households deposit their savings into financial institutions, which then use these funds to provide investment for businesses. This investment serves as an injection into the economy, allowing firms to expand and increase production.
The government also influences the circular flow of income by engaging in government expenditure (G), such as funding for infrastructure, public services, and welfare programs. At the same time, the government collects taxes (T) from both households and firms, which act as a withdrawal from the circular flow.
In an increasingly globalised economy, international trade also plays a vital role. A country earns export revenue (X) when it sells goods and services to foreign markets, which acts as an injection into the circular flow. Conversely, when domestic firms and households purchase imports (M) from foreign countries, this spending leaks out of the domestic economy as a withdrawal.
How an increase in productivity will affect its components
An increase in productivity leads to a reduction in production costs, making domestically produced goods and services more price competitive in international markets. As a result, the price of exports decreases, making Singaporean goods more attractive to foreign buyers.
If the demand for exports is price elastic, meaning that a decrease in price leads to a more than proportionate increase in quantity demanded, then total export revenue (X) will increase. This increase in export earnings serves as an injection into the circular flow of income, leading to higher national income and economic growth.
Higher productivity improves business profitability as firms can produce more output at a lower cost. This increased profitability encourages firms to invest in new technology, machinery, and capital equipment to further enhance efficiency.
As firms increase their investment expenditure (I), this acts as an injection into the economy, stimulating further economic activity. Additionally, greater investment in technology and infrastructure can have positive multiplier effects, leading to job creation and higher aggregate demand.
An increase in productivity can lead to higher employment levels and rising household incomes as firms expand and hire more workers. With higher disposable income, households may increase their consumption, including spending on imported goods and services.
As a result, import expenditure (M) is likely to rise, leading to a withdrawal from the circular flow of income. The extent of this increase in import spending depends on the marginal propensity to import (MPM)—the proportion of additional income spent on imports. If Singaporeans have a high preference for foreign goods, the rise in national income may
Conclusion
The circular flow of income provides a framework for understanding how different economic agents interact within an economy. Productivity growth plays a key role in shaping this flow, influencing the levels of exports, investment, and imports. Increased productivity enhances export competitiveness, leading to higher export revenue, which serves as an injection into the economy. It also boosts investment expenditure, further supporting economic growth. However, higher productivity may also lead to increased import expenditure, which acts as a withdrawal from the circular flow. While some leakages may occur, the overall impact of productivity growth is positive, as it drives economic expansion, increases national income, and enhances the standard of living. Therefore, sustained efforts to improve productivity will be crucial for long-term economic prosperity.
📘 June Holiday Economics Crash Course 2025
Want to Write Like a Top Scorer — Not Just Read Like One?
Model essays are helpful, but A Level success takes more than just reading. To score those elusive L3s and handle every CSQ twist with confidence, you need structure, strategy, and real feedback.
That’s what we do best at Economics at Tuitiongenius, Singapore’s most trusted economics tuition centre founded by Mr Eugene Toh — a name synonymous with top A Level economics tuition in Singapore.
🚀 Your June Game Plan: Learn Smart. Write Better. Score Higher.
Whether you're in JC1 preparing for Promos or JC2 pushing toward Prelims and A Levels, our high-impact crash course is designed to take your skills — and scores — to the next level.
🔍 What’s Inside:
📘 Content Crash Course (2 & 4 June 2025)
✔ Master 8 key Micro & Macro topics in just 12 hours
✔ Choose onsite learning or get lifetime access to recorded videos
✍️ Essay & CSQ Bootcamp (9 & 10 June 2025)
✔ Learn from 10 real A Level essays + 8 fully dissected CSQs
✔ Get live practice, proven structures, and powerful evaluation techniques
💥 Bundle Up & Save
Join both sessions and enjoy:
Over $1000 in savings
Printed materials shipped to your doorstep
Lifetime access to recordings
This is the most value-packed JC economics tuition option available this June.
📍 Whether you’re searching for economics tuition Singapore, online economics tuition, or expert guidance from a proven economics tutor — this is your moment to catch up and leap ahead.
🔗 tuitiongenius.com/june
📲 WhatsApp us at 8168 3986 — we’ll help you get started instantly.
Let’s make this June the turning point in your A Level journey.