(2020) A Level H2 Econs Essay Q1 Suggested Answer by Mr Eugene Toh (A Level Economics Tutor)
(2020) A Level H2 Econs Paper 2 Essay Q1
Disclaimer: The answers provided on our website is a 'first draft outline’ version of the answers provided for your convenience.
For the full, finalised answers, please click here to purchase a hard copy of the Comprehensive TYS Answers authored by Mr Eugene Toh and published by SAP. (The page might take awhile to load)
Search for “COMPREHENSIVE ANSWERS TO A LEVEL H2 ECONOMICS YEARLY EDITION” or “9789813428676” to purchase.
1. Discarded plastic and carbon emissions are among the biggest causes of pollution. The environmental damage to the air and water runs into billions of dollars. This affects not only our health but also our food supply.
Adapted from: Kimberly Amadeo, How Air, Water and Plastic Pollution Affect the Economy, 18 June 2019
(a) Explain how pollution leads to market failure. [10]
Define market failure & negative externalities
Market failure - When the free market / price mechanism fails to allocate resources efficiently
Negative externalities – Costs imposed on third parties who are not directly involved in the production or consumption of the good.
Explain how pollution via carbon emissions lead to market failure
Pollution via carbon emissions lead to market failure due to the presence of negative production externality
When firms carry out the production of goods & services, they will only take into consideration their own marginal private costs and benefits
Firms’ consideration of marginal private costs include various costs of production including rent, raw materials, labour etc
Firms’ consideration of marginal private benefits include the revenue they derive from the sale of goods & services
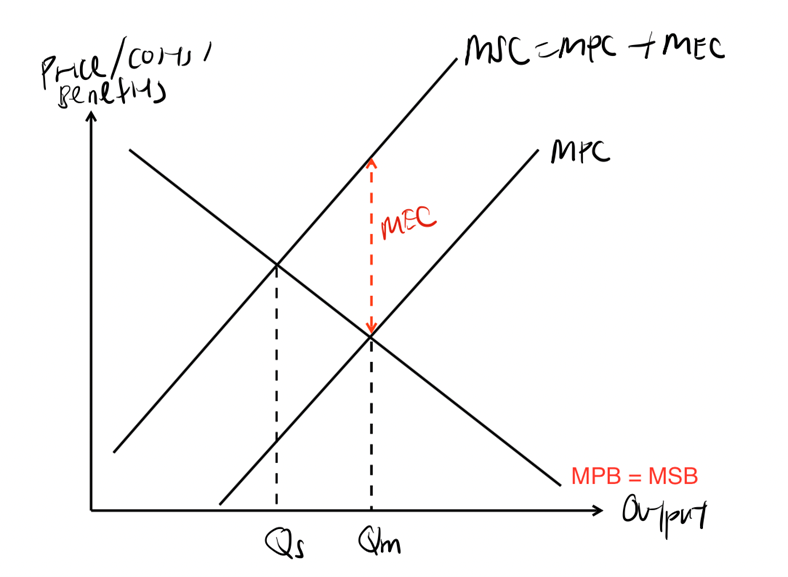
This fails to account for the negative externalities caused as a result of carbon emissions generated during production – this leads to presence of MEC, which causes MSC to diverge from MPC
MEC = Carbon emissions can result in air pollution – where the inhalation of carbon emissions can cause breathing difficulties / lung-related problems / bronchitis by people living in the country
As firms do not take into consideration the MEC, they produce at the market equilibrium output Qm where MPC = MPB instead of the socially optimal level of output Qs where MSC = MSB
This results in market failure due to overproduction
Explain how pollution via discarded plastic lead to market failure
Pollution via discarded plastic lead to market failure due to the presence of negative consumption externality
When individuals make use of plastic (e.g. bottles, bags), they only consider their own marginal private costs and benefits
Individuals’ consideration of marginal private costs include the cost of the plastic bottles / bags (which is low or non-existent most of the time)
Individuals’ consideration of marginal private benefits include convenience from the 1-time use of plastics
This fails to account for the negative externalities or MEC caused as a result of discarded plastics.
MEC = Discarded plastics can lead to water pollution – which can end up poisoning marine creatures and therefore affecting the food supply – affecting prices of food and individuals who consume such marine creatures whose health may be affected through the consumption of contaminated food
As individuals who use plastics do not take into consideration the MEC, they consume the market equilibrium output Qm where MPC = MPB instead of the socially optimal level of output Qs where MSC = MSB
This results in market failure due to overconsumption
(b) Discuss the extent to which government policy measures are likely to address this market failure. [15]
Taxes
The government can impose a tax on firms causing carbon emissions to correct the market failure from overproduction
This can be done by implementing a tax equivalent to the MEC
This shifts the MPC to the left, forcing firms to internalise the external cost
Production will thus be reduced from Qm to Qs, addressing the problem of market failure
Ev – In reality, governments may find it hard to estimate the MEC to accurately implement a tax to correct the overproduction problem. In addition, there may be the potential problem of carbon leakage where firms may simply move their production to neighbouring countries.
Legislation
The government may pass laws to ensure firms / individuals carry out proper disposal of plastics to ensure that plastics are not disposed improperly into water sources causing contamination of marine food sources
Individuals / firm failing to abide by such legislation can be penalised via fines
This will reduce the improper disposal of plastics
Ev – There is always a problem with enforcement. Enforcement not properly policed is ineffective, while yet can be costly to properly deploy manpower to ensure enforcement.
Education campaigns
Encourage reuse / reduction of use of plastics through education campaigns to encourage individuals to be more civic-minded
As individuals cut back on consumption of plastics or reuse existing plastics – this will reduce the amount of plastics ending up in water sources – reducing pollution levels and thus reduce negative externalities generated
Ev – It is hard to measure the success of education campaigns to properly determine if such campaigns are successful
Found our TYS answers useful?
Maximise your A-Level H2 Economics preparation with the ETG A-Level H2 Economics TYS Crashcourse! Perfect for students looking to enhance their skills in both essay and case study analysis, this comprehensive 3-day crashcourse will cover over 60 essay questions and 20 case studies from the A-Level Economics Ten-Year Series. Whether you're attending onsite or via Zoom, our experienced tutors will guide you through the intricate demands of H2 Economics, offering expert feedback and graded answers. For the best economics tuition in Singapore, sign up now to secure one of the limited onsite seats!